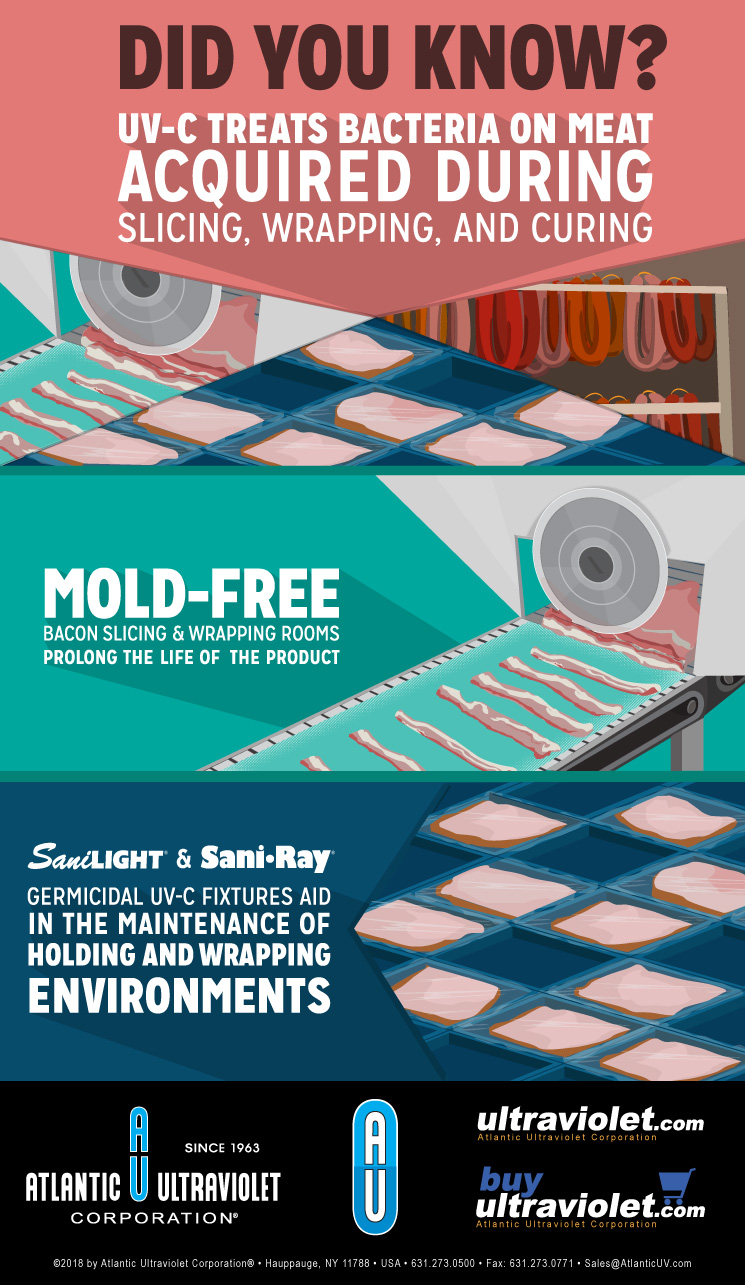
Uv Light Meat Processing

They emit uv c energy at 254 nanometers a wavelength that s lethal to virtually all microorganisms with proper dosage.
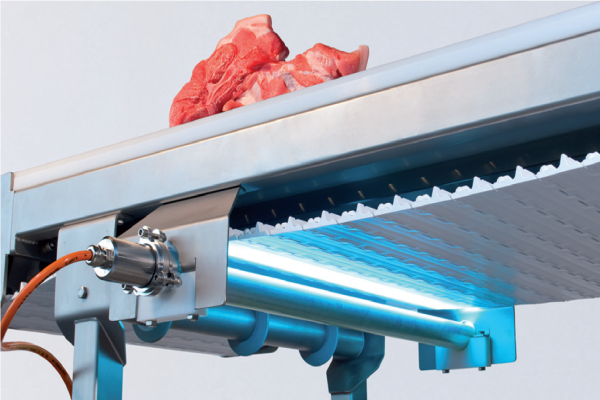
Uv light meat processing. The installation of a highly efficient uv disinfection system. Hanovia uv disinfection systems are compact and can be easily incorporated into a number of meat processing applications including treatment of wash water brine chillers meat marinade and pickle injectors and also for disinfecting wastewater for reuse in processing. We offer a custom fit exact match for your production conditions coordinated solution that is easy to install and inexpensive from the emitter up to the complete uv module for large ventilation systems. Ultraviolet light uv light holds considerable promise in food processing as an alternative to traditional thermal processing.
The introduction of germicidal ultraviolet uv c technologies into meat processing facilities directly equates to a healthy and safe working environment as well as higher quality products. Paskeviciute et al 2011. One of the disadvantages of continuous uv light is the induction of oxidation processes in meat which afterward changes its sensorial properties paškevičiūtė and lukšienė 2009. Surface application of uv light after production can offer an attractive alternative method to eliminate or control the growth of post processing contamination.
Its applications include pasteurization of juices post lethality. Other promising uses of uv light are the disinfection of air and water used in dairy plant and surface decontamination of food contact surfaces and packaging materials. High vulnerability to viruses and germs in the meat processing industry. Uv light can play a critical role in brown discolouration of meat since it encourages metmyoglobin formation.
According to the fda uv c at 200 to 280 is within the germicidal range as it effectively inactivates bacteria and viruses this is due to dna mutations that occur when uv is light is absorbed by dna molecules.